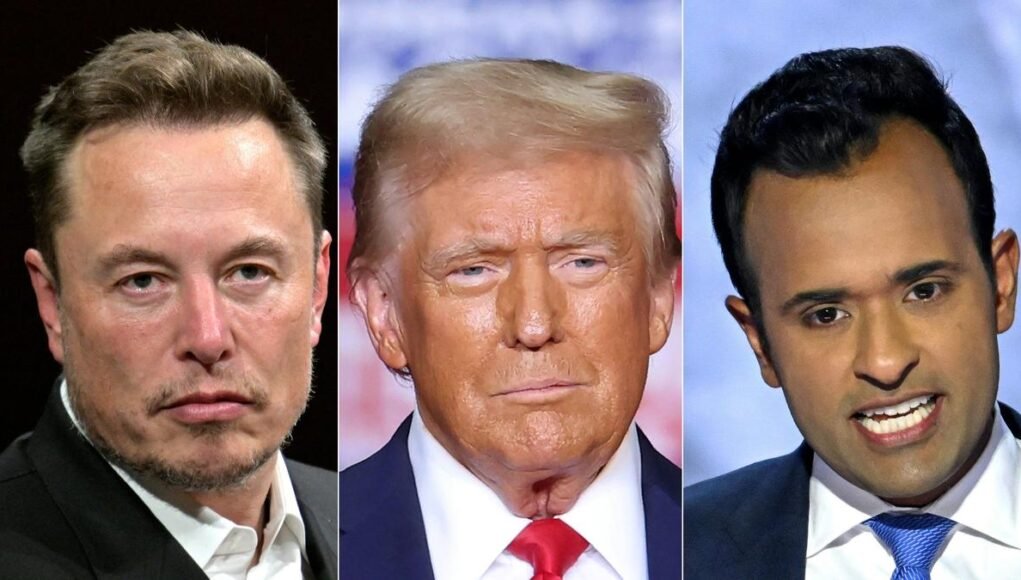
President-elect Donald Trump’s decision to appoint tech billionaire Elon Musk and biotech entrepreneur Vivek Ramaswamy to lead the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE). It explores the rationale behind the appointments, the duo’s background, their alignment with Trump’s views on bureaucracy reduction, and the implications of such an initiative. Furthermore, it compares past efforts like Reagan’s Grace Commission and discusses potential impacts, including the controversial Schedule F initiative.

Main Ideas in Points
1. Context of the Appointment
- On November 12, 2024, President-elect Donald Trump announced the creation of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE).
- Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy were chosen to lead the department, tasked with reducing bureaucracy, eliminating wasteful expenditures, and restructuring federal agencies.
2. About the Appointees
- Elon Musk:
- CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, known for groundbreaking contributions to electric vehicles and space exploration.
- His ventures include Starlink, offering satellite-based internet, especially in remote regions.
- Experienced in dealing with bureaucracy, including legal challenges during his acquisition of Twitter, which he restructured extensively after purchase.
- Vivek Ramaswamy:
- Founder of Roivant Sciences, involved in innovative biotech ventures.
- Transitioned to politics after business success, running for the Republican presidential nomination in 2024.
- Advocates for dismantling federal agencies and restructuring intelligence units to curb regulatory overreach.
3. Reasons Behind the Selection
- Both appointees share Trump’s philosophy of minimizing government bureaucracy and regulatory capture.
- Musk proposed significant federal budget cuts during a Trump rally, aligning with the president-elect’s fiscal goals.
- Ramaswamy’s campaign emphasized dismantling redundant agencies and streamlining government operations.
4. Historical Precedents
- Similar efforts include Ronald Reagan’s Grace Commission (1982), which proposed 2,500 recommendations for reducing waste and inefficiency in federal agencies.
- Most recommendations from the Grace Commission were not implemented due to a lack of congressional approval.
5. Challenges and Limitations
- DOGE’s work might be limited to creating recommendations, much like the Grace Commission.
- Implementation of the proposed changes depends on congressional approval, which may face political resistance.
6. Potential Impact with Schedule F
- Trump’s Schedule F initiative could complement DOGE’s efforts by reclassifying federal employees, making it easier to dismiss them at the president’s discretion.
- This would grant unprecedented executive control, sparking concerns over undermining the non-partisan nature of civil services.
7. Criticism and Debate
- Supporters argue such reforms are essential to counteract inefficiencies and curb the influence of entrenched bureaucracies.
- Critics warn these moves risk dismantling the modern civil service system, jeopardizing its impartiality and stability.
8. Timeline and Scope
- DOGE’s work is set to conclude by July 4, 2026, focusing on recommending actionable changes rather than directly executing reforms.
The appointment of Musk and Ramaswamy to DOGE reflects Trump’s ambition to overhaul federal bureaucracy using a corporate-like approach. However, the success of this initiative depends on navigating political hurdles and balancing the need for efficiency with preserving the integrity of civil services.